On June 19, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic, Baxdela® (delafloxacin), for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI). Approval of Baxdela®, which is effective against resistant organisms such as MRSA, will provide physicians another tool to combat growing antibiotic resistance.
Approximately 3 million patients are hospitalized each year in U.S. with ABSSSI, most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These patients often present clinical challenges due to multiple infections or unrelated underlying conditions. This makes selecting the appropriate antibiotic difficult. Baxdela®, like Sivextro® (tedizolid) and Zyvox® (linezolid), is orally bioavailable, providing for more flexible dosing and allowing hospitalized ABSSSI patients to return home more quickly.
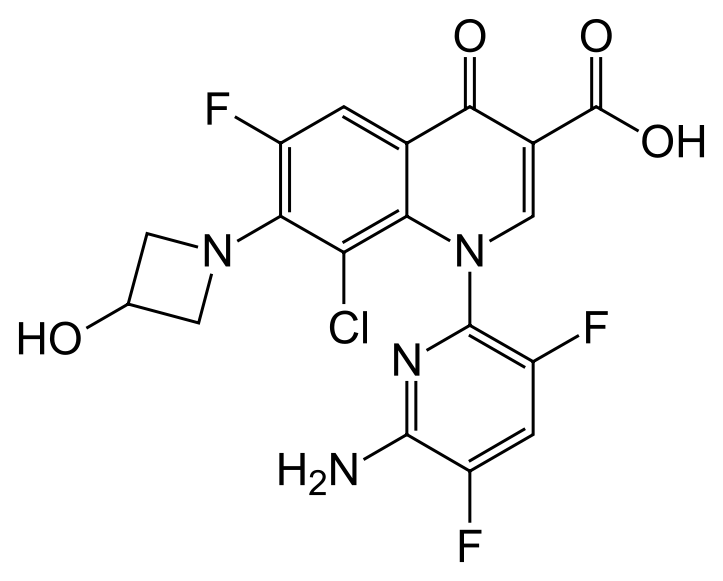
Baxdela® (1-(6-amino-3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-8-chloro-6-fluoro-7-(3-hydroxyazetidin-1-yl)4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol salt) is an orally available bacterial topoisomerase inhibitor, which is required for bacterial DNA repair and replication.
Both oral and injectable Baxdela® demonstrated a clinically meaningful response over vancomycin in combination with aztreonam in patients with ABSSSI. The CDC estimates that there were approximately 80,000 cases of antibiotic resistance Staphylococcus aureus in 2013, resulting in 11,000 deaths (a mortality rate of nearly 14%). Being newly approved, Baxdela® leaves behind six other drug candidates in Phase 3 trials with demonstrated activity against resistant organisms.
